
With your phone take pictures of you experiment, like we did of ours.

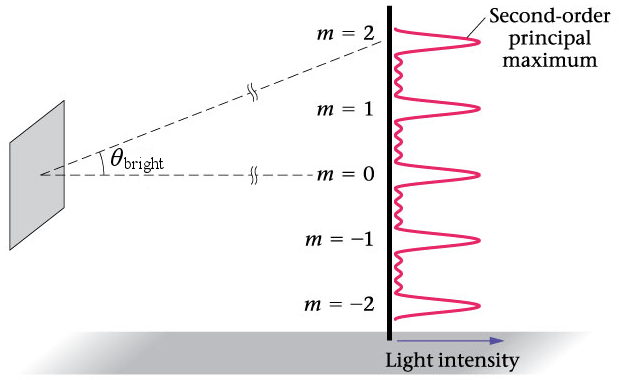
Use a pencil or pen to mark the central maximum (brightest spot in middle) and the first order maxima on either side. You will be able to see the central maximum and the first and the second order maxima. Make sure the grating is perpendicular to the laser beam measurements are not very accurate if the maxima are not centered on the central maximum. Direct the laser beam through the diffraction grating. m=1 First order maxima Laser en Central Maxima L Diffraction Grating 7. In the picture below you can see our experimental set-up. Use the second binder clip to keep the laser pointer level with the floor or table. Use the binder clip to maintain the laser pointer in the ON position. Measure the distance between the diffraction grating and the wall (L) 6. Use a binder clip to hold the diffraction grating and position the grating parallel with the wall. Lay the meter stick or ruler on a table or the floor so the 0 meets the wall. Tape a blank sheet of white paper to the wall. Show the calculations that your group has decided to be correct here and then indicate your value for d: d=2*10^-6 2. Determine the distance between the slits (d) in m. The number of lines/mm is indicated on the diffraction grating. A diffraction grating consists of a large number of parallel, closely spaced slits. In addition you will need a metric ruler or a meter stick, several blank sheets of white paper and tape.

The laser pointer is powered by 3 small batteries, do not keep it on for a long time or you will drain the batteries and the laser spot will not be bright enough to perform the experiment. To complete this lab you will need the laser pointer, the diffraction grating with lines of known separation and the binder clips provided in your lab kit. Never look directly into a laser or let the laser beam shine directly or reflect into anyone's eye.

Warning: The laser beam is intense enough to burn the retina of your eye. To determine the wavelength of laser light emitted from a laser pointer. To investigate the interference pattern created when laser light passes through a diffraction grating 4. To explore light diffraction and interference 3. To observe how light waves behave when they pass through narrow slits 2. What is the intensity of the transmitted light through P 2 and what is the direction of polarization? (f) Finally, she crosses the two polarizers at 9 0 ∘ again and places a liquid crystal sample in between the two crossed polarizers that acts as a perfect polarizer at an angle of 3 0 ∘ with respect to the first polarizer.Lab 4: Diffraction and Interference of Light - Interference Pattern Created by a Diffraction Grating Objectives of this lab: 1. (e) Starting with both polarizers oriented vertically, she rotates P 2 3 0 ∘ and shines unpolarized light of intensity I 0 onto P 1 . The m = 0 central fringe would eject elecrons from the metal, but for the following only consider the m = 1 bright fringes. The light that emerges from the grating then falls on a wide, flat sheet of metal with a work function of 2.20 eV. A beam of light consisting of all wavelengths between 400 nm and 650 nm is incident on a transmission diffraction grating that has a slit spacing of 1.33 × 1 0 − 6 m.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
